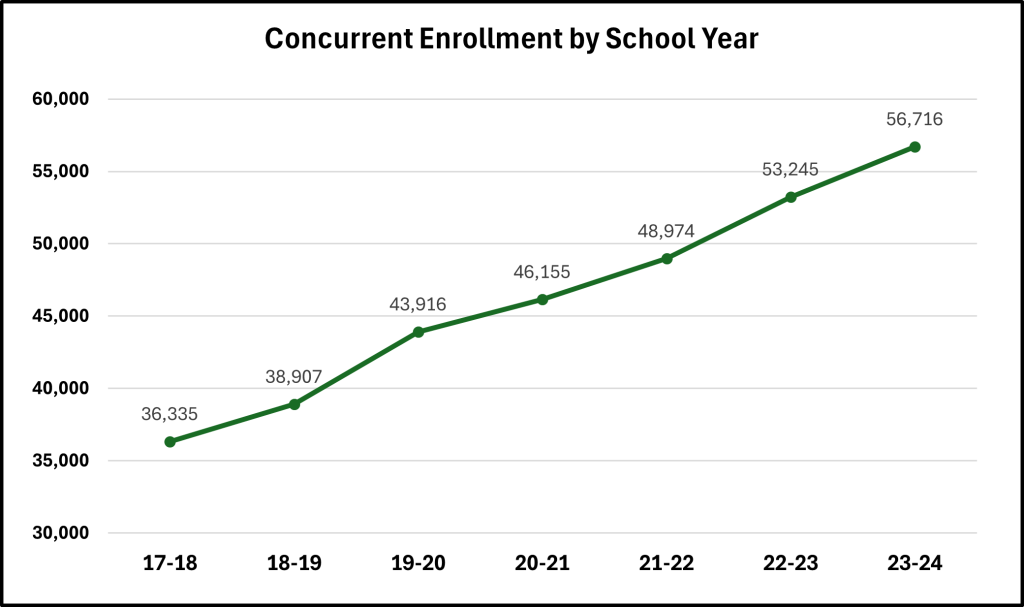
Concurrent Enrollment (CE) is a long-standing program that connects Utah’s public schools and higher education institutions, allowing high school students to earn credit for both high school and college in the same course. In the 2024 school year, more than 56,000 Utah students participated (or roughly 26 percent of all high schoolers), making CE a central part of the state’s early college pathway strategy.
The Utah State Board of Education (USBE) and the Utah Board of Higher Education (UBHE) jointly oversee the state’s CE program. Local Education Agencies (LEAs) contract with higher education institutions to provide courses, ensuring accountability and statewide consistency. Classes are taught by either college faculty or qualified high school teachers approved by partnering higher education institutions. CE credits are applied to both high school graduation requirements and future college degrees or certificates.
Participation and Funding
CE participation has grown steadily, increasing nearly 30% in the last five school years and an average of 7.5% per year since 2018. Participation jumped nearly 13% in 2019-20 alone, likely because of COVID-19 and the shift to online learning which made CE courses more accessible to students statewide.
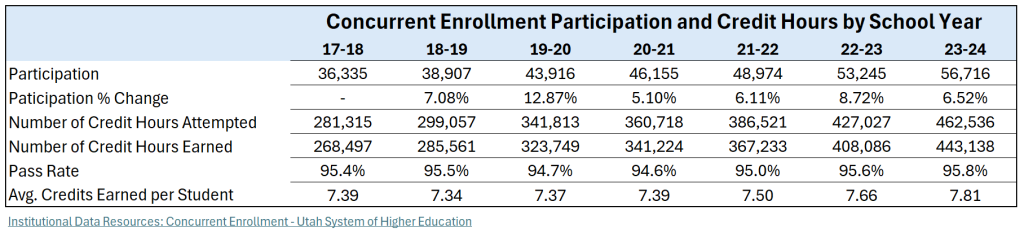
In the 2024 school year, students successfully earned over 443,000 credit hours, with a passage rate mirroring the average at 95%. At the same time, the statewide average for credit hours earned has incrementally increased to7.8, up almost half a credit hour from 2018. These results show that growth in participation has not diluted success, with students increasing engagement and maintaining strong outcomes.
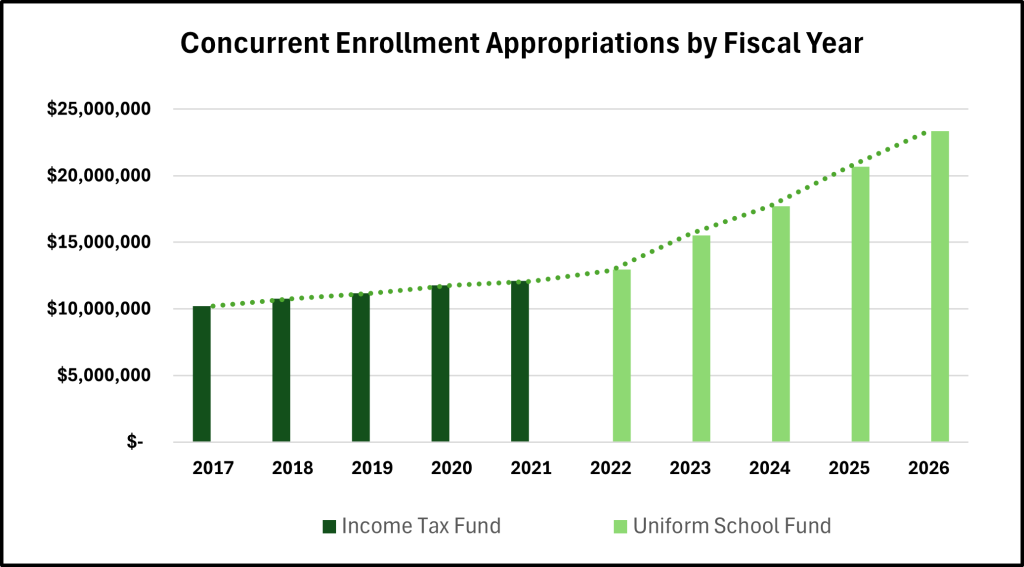
The state pays for CE through a combination of enrollment growth and the WPU value. During the 2020 Fifth Special Session, the Legislature passed H.B. 5011, “WPU Value Increase Guarantee” which raised the WPU value by an additional 4 percent and directly tied CE funding to adjustments in the WPU value. Before this, the annual percentage funding increase averaged 4.35 percent, whereas since the WPU Value Increase Guarantee, the average annual increase has risen to 14.12 percent. The CE program budget (which is part of the Minimum School Program) is $23.4 million for Fiscal Year 2026.
State appropriations for CE are distributed based on who bears the primary cost of instruction. The allocation formula is outlined in UCA 53F-2-409:
| Instructor | Funding to LEA | Funding to Higher Education |
|---|---|---|
| High School Teacher | 60% | 40% |
| College Faculty | 40% | 60% |
For instance, when a Higher Education institution primarily bears the cost of instruction, the State Board of Education distributes 60% of the appropriated state funds to State Board of Regents, and 40% to the LEAs. While this model is flexible in its design, since 2018, LEAs have received 60% of the appropriated funding for the CE program.
Alongside legislative appropriations, students pay a small tuition amount directly to the higher education institution offering the CE course. UCA 53E-10-305 provides a statutory cap of $30 per credit hour for courses that earn college credit (with lower thresholds outlined for students in certain socioeconomic conditions). Current practice across all Utah System of Higher Education institutions is $5 per credit hour for CE courses. Most CE courses count for three credit hours, so students typically pay $15 per course. The statute also permits institutions to charge a one-time admission fee for CE students. Institutions retain student tuition revenue, which is separate from the state’s appropriation for the program.
According to USHE Concurrent Enrollment Dashboard, Utah students saved a total of $110.6 million in tuition by taking CE courses from Degree Granting Institutions and Technical Colleges. On average, this participation saves students approximately $950 per three-credit course based on 2026 tuition rates.
Recent Legislative Updates
- S.B. 102, “Public Education Reporting Amendments” (2025 General Session) requires a review of the CE program by the Education Interim committee every five years beginning in FY 2028.
- H.B. 493, “Concurrent Enrollment Participation Amendments” (2024 General Session) allows students to participate in a broader range of online courses offered statewide, not limited to offerings from the LEA’s designated institution of higher education.
- H.B. 22, “Concurrent Enrollment Revisions” (2024 General Session) amends criteria for certifications offered through the CE program and requires scholarships to be awarded for certain CE students who earn certificates.
Concurrent Enrollment has evolved from a foundational partnership into an increasingly vital component of Utah’s education system. Robust participation and high course passage rates have saved Utah’s students millions of dollars, providing a financial head start as they enter the next phase of their educational careers. Recent legislative changes reinforce the state’s commitment to advanced education by expanding access to online courses and providing additional financial support for students as they continue onto higher education.